Financial data breaches are on the rise, posing a significant threat to businesses and individuals alike. At CFO Insights, we’ve seen firsthand the devastating impact of cyberattacks on financial institutions.
In this post, we’ll explore the current landscape of cybersecurity in finance and provide practical steps to protect your organization’s valuable data. We’ll also delve into emerging technologies that are shaping the future of financial cybersecurity.
Financial Data Under Siege: The Evolving Cybersecurity Landscape
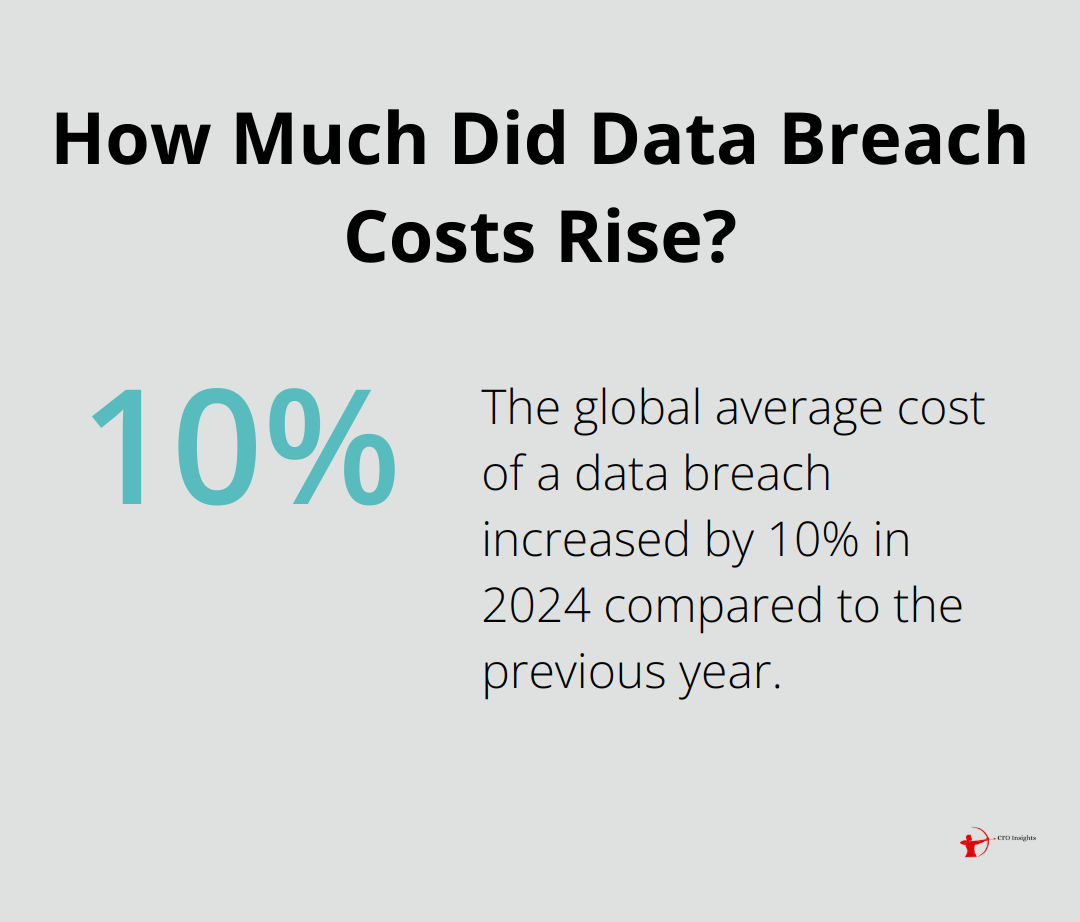
The financial sector faces an unprecedented wave of cyber threats. In 2024, the global average cost of a data breach reached the highest total ever, with a 10% increase over the previous year. This figure underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures in finance.
High-Profile Breaches Rock the Industry
Recent years have witnessed several alarming breaches. In 2022, Revolut (a digital banking platform) suffered an attack that exposed the personal data of over 50,000 customers. Similarly, Medibank (one of Australia’s largest health insurers) fell victim to a breach that compromised the data of 9.7 million customers, including sensitive financial information.
These incidents serve as stark reminders of the vulnerabilities in our financial systems. They highlight the urgent need for organizations to strengthen their defenses against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
The Diverse Threat Landscape
Financial institutions confront a diverse array of cyber threats. Ransomware attacks have surged, with a 238% increase targeting the finance sector from the beginning of February to the end of April 2020. These attacks not only disrupt operations but also pose significant reputational risks.
Phishing remains a persistent threat, with a significant portion of attacks linked to financial institutions. These attacks often serve as gateways for more severe breaches, exploiting human vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive systems.
AI-Powered Attacks: A New Frontier
The sophistication of cyberattacks has reached new heights with the integration of artificial intelligence. AI-driven techniques in the attack process allow attackers to initiate attacks on a larger scale, making them particularly challenging to detect and mitigate.
This evolution in attack methodologies demands a corresponding advancement in defense strategies. Financial institutions must leverage AI and machine learning in their cybersecurity efforts to stay ahead of these intelligent threats.
The Role of Proactive Defense
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, financial institutions must adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity. This includes implementing robust security measures (such as multi-factor authentication and encryption), conducting regular security audits, and investing in employee training programs.
Organizations should also consider partnering with cybersecurity experts (like CFO Insights) to develop comprehensive security strategies tailored to their specific needs and risk profiles. These partnerships can provide valuable insights and resources to help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and protect their sensitive financial data.
Fortifying Financial Data: Essential Cybersecurity Measures
In today’s digital landscape, protecting financial data is paramount. Financial institutions must implement key measures to safeguard their sensitive information and maintain client trust.
Strengthening Access Controls
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is no longer optional-it’s a necessity. Banning the use of bad passwords, blocking legacy authentication, and training employees on phishing can help prevent automated attacks. Financial institutions should implement MFA across all access points, including employee accounts, customer portals, and third-party integrations.

Access controls should follow the principle of least privilege, granting users only the permissions necessary for their roles. Regular access reviews and prompt deprovisioning of accounts for departing employees are essential steps in maintaining a secure environment.
Encryption: The Last Line of Defense
Encryption acts as a critical safeguard for financial data, both at rest and in transit. The Australian Cyber Security Centre recommends using encryption to protect data from unauthorized access or manipulation when communicated over network infrastructure. This includes HTTPS implementation for web applications and secure protocols like TLS for data transfers.
For data at rest, financial institutions should use strong encryption algorithms and securely manage encryption keys. This ensures that even if data is compromised, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Continuous Security Validation
Regular security audits and penetration testing identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. The frequency of these assessments should align with the organization’s risk profile and regulatory requirements.
Penetration testing should simulate real-world attack scenarios, including social engineering attempts and advanced persistent threats.
Cultivating a Security-First Culture
Employee training is often overlooked but prevents many cyber incidents. The 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report found that 74% of breaches involved the human element (including errors and social engineering).
Financial institutions should implement comprehensive security awareness programs that go beyond annual compliance training. Regular phishing simulations, security newsletters, and interactive workshops can help employees recognize and respond to potential threats effectively.
Creating a culture where security is everyone’s responsibility not only enhances an organization’s security posture but also demonstrates a commitment to protecting client data-a key differentiator in the financial sector.
These measures significantly reduce risk exposure and build a robust defense against cyber threats. However, cybersecurity requires constant vigilance and adaptation to new threats and technologies. As we look to the future, emerging technologies promise to revolutionize financial cybersecurity even further.
How New Technologies Reshape Financial Cybersecurity
AI-Powered Threat Detection: Staying Ahead
AI and cybersecurity has become crucial for safeguarding sensitive financial data and maintaining trust in the industry. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate a cyber attack.

AI-driven behavioral analytics creates a baseline of normal user behavior and flags deviations that could signal a compromised account or insider threat. For example, if an employee accesses sensitive financial records outside their usual working hours (or from an unfamiliar location), the system immediately alerts security teams for further investigation.
Blockchain: Securing Transactions Beyond Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology finds new applications in financial cybersecurity. In industries where data verification is crucial, such as healthcare and finance, blockchain can provide a tamper-proof record of transactions and interactions.
Financial institutions implement blockchain for identity verification and know-your-customer (KYC) processes. This enhances security and streamlines operations.
Blockchain also enables secure data sharing. Financial institutions share critical information about cyber threats without compromising sensitive data. This collaborative approach strengthens the entire financial ecosystem against common threats.
Cloud Security: Scalable Protection for Financial Data
The migration of financial services to the cloud accelerates, bringing opportunities and challenges for cybersecurity. Cloud providers offer robust security features, but financial institutions must leverage these tools effectively.
Cloud access security brokers (CASBs) act as a security layer between an organization’s on-premises infrastructure and cloud providers, offering visibility into cloud usage and enforcing security policies.
Financial institutions embrace zero-trust architectures in their cloud environments. This approach assumes no user or device is trustworthy by default, requiring continuous verification. It proves particularly effective in today’s distributed work environments where employees access financial data from various locations and devices.
Biometric Authentication: The New Frontier of Access Control
Biometric authentication methods gain traction in financial services, offering a balance of security and user convenience. Fingerprint scans, facial recognition, and voice authentication provide a more robust alternative to traditional passwords.
Recent research indicates that approximately 72% of global consumers now prefer biometric authentication over traditional PIN security. Financial institutions respond to this demand.
However, implementing biometric systems requires care. They must pair with strong data protection measures to safeguard the biometric information itself. Multi-modal biometric systems (combining two or more biometric factors) enhance security further.
Final Thoughts
Proactive measures are essential in cybersecurity finance. The financial sector faces unprecedented challenges with cyber threats growing in sophistication and frequency. Organizations must protect their assets and maintain client trust by staying ahead of these threats.

CFOs play a pivotal role in driving cybersecurity initiatives. They allocate resources for cybersecurity measures and work closely with IT teams to understand risks. CFOs must prioritize investments and ensure cybersecurity strategies align with overall business objectives.
At CFO Insights, we understand the complexities of managing cybersecurity in the financial sector. Our fractional CFO services help organizations navigate these challenges. We work with businesses to develop comprehensive strategies that protect financial assets and support growth initiatives.




